Anticholinergic Burden Calculator (ACB2) (HP104)
Anticholinergic Burden Calculator (ACB2) (HP104)
Overview/Purpose
This protocol will inform clinicians of the anticholinergic burden score that the patient has, as well as the drugs that contribute to the score.
What does it do?
- Based on the ACB Scale referenced in NICE NG97,
- Accurately assesses all currently prescribed medications against updated ACB categories (2012) and calculates the score
- Shows clinicians which medications are contributing to the total score and by how much,
- Allows the clinician to code the ACB Scale in the notes,
- Gives advice about the ACB Scale to encourage deprescribing,
- No need to manually input all medications into an external calculator or cross reference with paper tables.
Why is it important?
Some medications have anticholinergic properties which contribute to memory loss, dementia, falls, urinary symptoms and even early death. Many common medications carry this anticholinergic effect and it is cumulative; the more you are on, the more the effect. This has been quantified in several scoring systems, including the Anticholinergic Cognitive Burden or ACB Scale (2008, revised in 2012), with many drugs being assigned a score of 1,2 or 3.
This protocol is run manually be the clinician. It calculates the score and seeks to support deprescribing decisions when performing medication reviews, including the more complex Structured Medication Reviews. The evidence for harm from these medications is more pronounced in those aged 65 or more where the calculator is most useful.
What does it look like?
When launched the protocol appears with the following information:
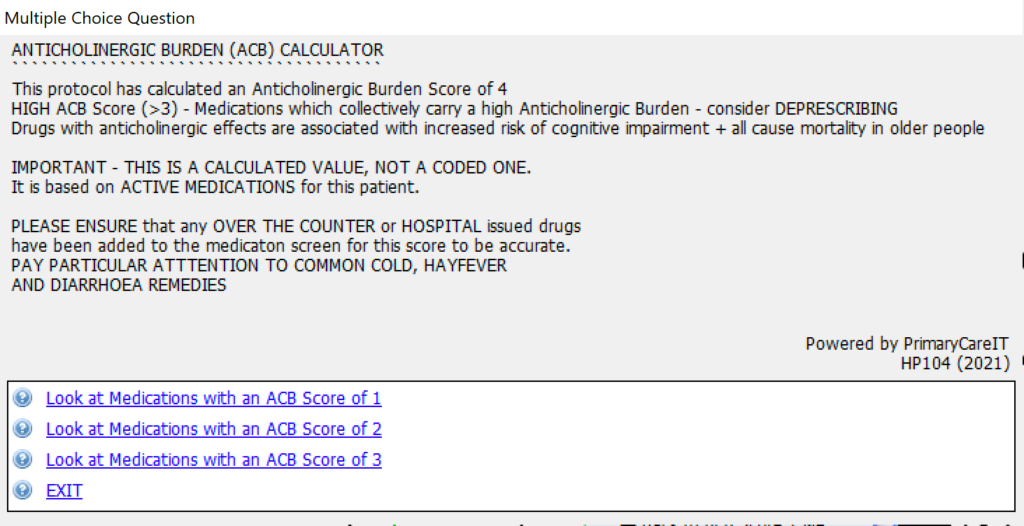
If you click on the links to the medicines with different scores you will see:
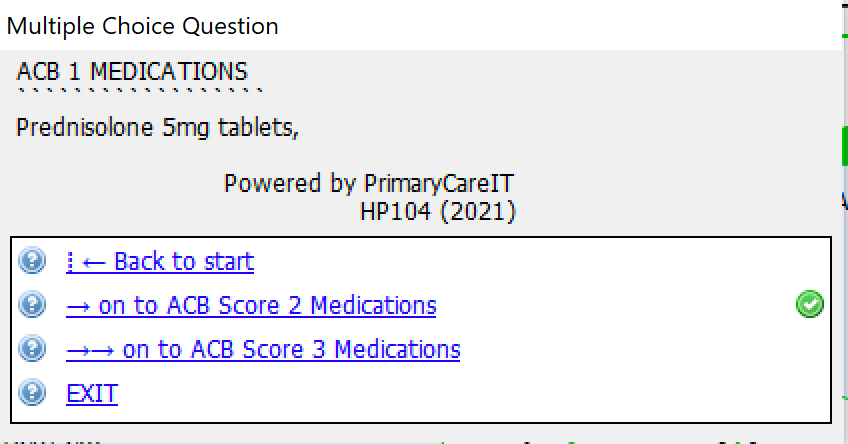
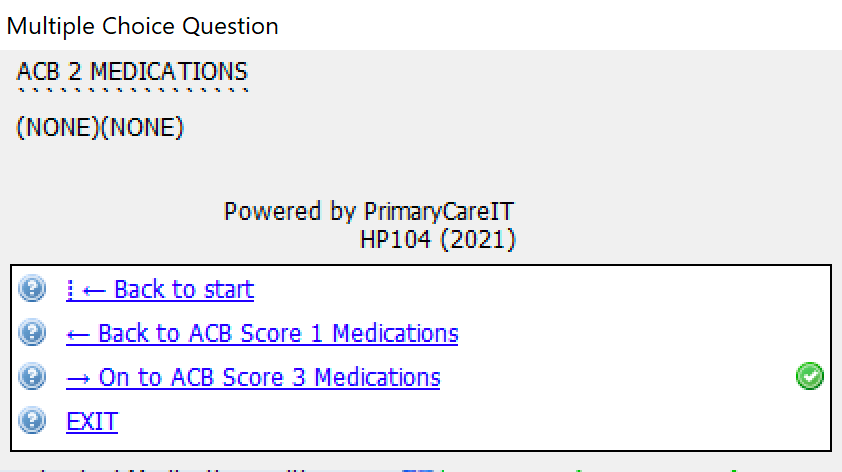
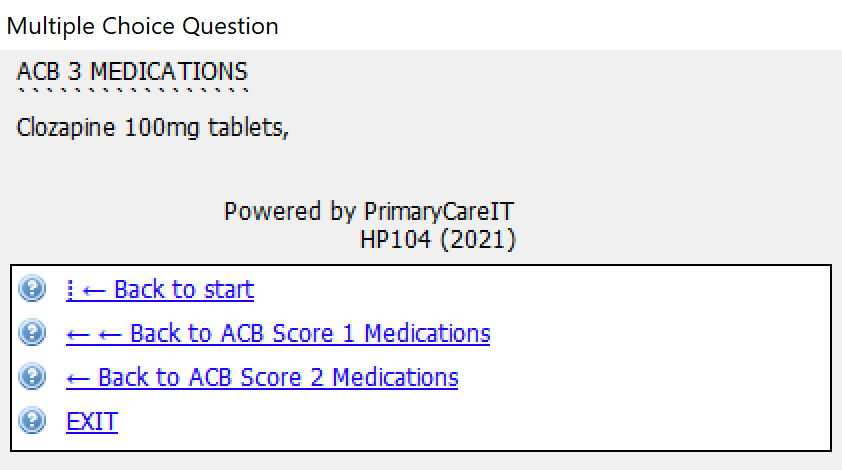
System Dependencies:
This protocol is dependent on accurate coded information within EMIS web, contemporaneously recording medication issues.
System Trigger:
Manually using F12 or using the OneLauncher Prescriber. See our separate article adding protocols to the Protocol Launcher (F12) if you need help with doing this.
Fitting your practice
Your team need to know that this protocol can be launched manually using F12. This may be a useful protocol to highlight after working your way through the QI standards for medication reviews.
Related Articles
Anticholinergic Burden Awareness alert (ACB2) (HP103)
Purpose: This protocol will inform clinicians of the anticholinergic burden score that the patient has, as well as the drugs that contribute to the score via a protocol alert. What does it actually do? Some medications have anticholinergic properties ...Lipid checking protocol (HP015)
Lipid Checking Protocol (HP015) Overview/Purpose This Lipid Checking Protocol is a protocol for EMIS Web, which has been designed to guide users through managing cholesterol results and to understand the context of the results for the patient that it ...Autocorrect height tool (HP035)
Purpose: This protocol will highlight if a very small height has been entered for a patient (in metres rather than in centimetres) which can adversely affect the calculation of BMI What does it actually do? When entering a height in EMIS there is no ...Safeguarding Information (HP011)
Safeguarding information (HP011) Overview/Purpose This protocol will display your local safeguarding information within a Protocol Alert for all children and any vulnerable adults What does it do? Highlights the existence of safeguarding codes ...NG12 Cancer Recognition - PSA Radar (HP197)
NG12 Cancer Recognition - PSA Radar (HP197) Overview/Purpose The Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) radar is designed to improve the detection of prostate cancer and to spot progression of established prostate cancer. The alert informs a user when ...